Dimensioning of control valve - Part 2 STEAM & GAS

We complete the technical notes for proper sizing of the DN of a valve with the following types of fluid: saturated steam, subsonic and sonic gases and vapors.
D) Saturated steam
with the following formula:
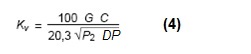
where:
- G = flow rate in Kg / h
- C = 1 + 0.0013 (t1 - t2)
- t1 = saturated steam temperature @ P1 pressure
- t2 = saturated steam temperature @ P2 pressure
- P1 = upstream absolute pressure in kPa
- P2 = downstream absolute pressure in kPa
- DP = pressure drop in kPa (P1-P2)
E) Gas and vapors
For these fluids, we have to distinguish two flow regimes: subsonic and sonic.
Subsonic regime
where:

and when do not reach the critical pressure ratio 
when the flow reaches the speed of sound.
Flow rate:
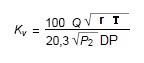
where:
- Q = flow rate in Nm3 / h @ 0 °C
- r = density in kg / dm3 @ 0 °C and atmospheric pressure
- P2 = downstream absolute pressure in kPa
- DP = pressure drop in KPa
- T = absolute temperature upstream in °K
Mass flow:
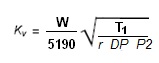
where:
- W = flow rate in kg / h
- r = density in kg / dm3 @ 0 °C and atmospheric pressure
- P2 = downstream absolute pressure in kPa
- DP = pressure drop in KPa
- T1 = absolute temperature upstream in °K
Sonic regime

and reaching or exceeding the critical pressure ratio 
ie the flow reaches the speed of sound
Flow rate:
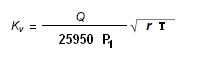
where:
- Q = flow rate in Nm3 / h @ 0 °C
- r = density in kg / dm3 @ 0 °C and atmospheric pressure
- P1 = upstream absolute pressure in kPa
- T = upstream absolute temperature in °K
Mass Flow:
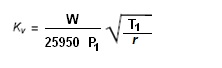
where:
- W = flow rate in kg / h
- r = density in kg / dm3 @ 0 °C and atmospheric pressure
- P1 = upstream absolute pressure in kPa
- T1 = upstream absolute temperature in °K
The technical notes indicated above are a summary of the general theory of fluid thermodynamics.
Our technicians are available to select and properly calculate the suitable control valve.
Posted in: Technical Library
